Understanding Torn Meniscus Recovery

A torn meniscus is a common knee injury that occurs when the cartilage in the knee joint tears. The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber and helps to stabilize the knee joint. A torn meniscus can occur due to a sudden twisting or impact injury, or it can develop gradually over time due to wear and tear.
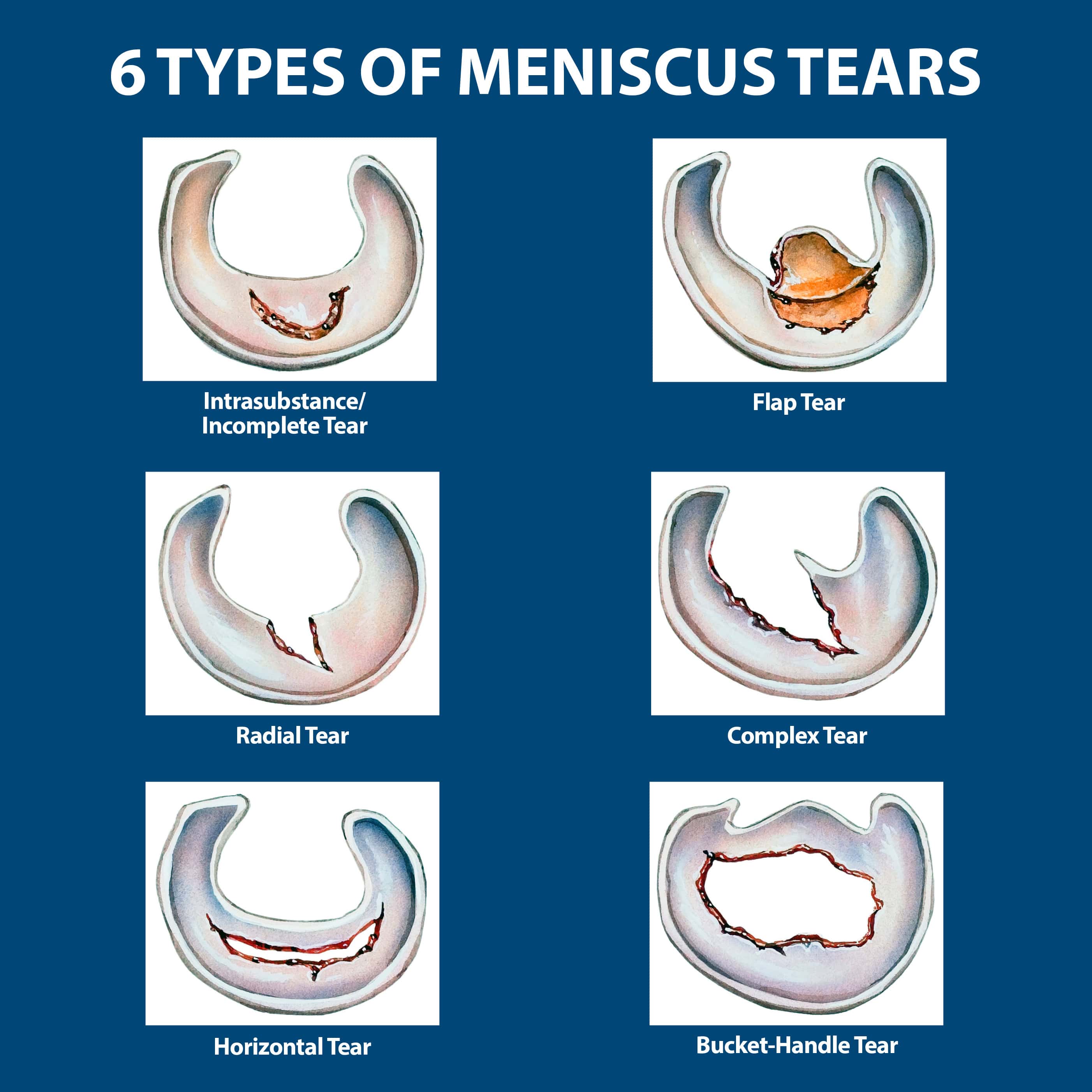
Types of Meniscus Tears and Severity
The severity of a meniscus tear can vary depending on the size and location of the tear. Meniscus tears are classified based on their location and shape:
- Horizontal tear: This type of tear runs horizontally across the meniscus, often occurring due to wear and tear.
- Vertical tear: This type of tear runs vertically along the meniscus, often caused by a twisting or impact injury.
- Radial tear: This type of tear runs from the outer edge of the meniscus to the inner edge, often caused by a twisting or impact injury.
- Degenerative tear: This type of tear occurs due to wear and tear over time, often in older individuals.
Factors Influencing Recovery Time
Several factors can influence the recovery time for a torn meniscus, including:
- Age: Older individuals may take longer to recover from a torn meniscus due to decreased blood supply to the meniscus, which can slow down healing.
- Fitness level: Individuals who are more physically active may have a faster recovery time due to their increased muscle strength and flexibility.
- Tear location: Tears in the outer portion of the meniscus tend to heal better than tears in the inner portion, as the outer portion receives more blood supply.
- Treatment: The type of treatment received can also affect recovery time. For example, surgery may require a longer recovery time than non-surgical treatment.
General Timeline for Recovery
The recovery time for a torn meniscus can vary depending on the severity of the tear and the type of treatment received. However, a general timeline for recovery may include the following milestones:
- First few days: Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are recommended to reduce pain and swelling.
- First week: Physical therapy may be initiated to improve range of motion and strength.
- Second to fourth week: Continued physical therapy to regain full range of motion and strength.
- Fourth to sixth week: Gradual return to activity, starting with low-impact activities and gradually increasing the intensity.
- Six to twelve weeks: Full return to activity, depending on the severity of the tear and the individual’s progress.
Treatment Options and Procedures: Torn Meniscus Recovery Time
Torn meniscus recovery time – A torn meniscus is a common injury that can occur due to a sudden twisting or forceful impact on the knee. The treatment options for a torn meniscus vary depending on the severity of the tear, the individual’s age, activity level, and overall health. Treatment options can range from conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to surgical interventions.
Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative treatment options are often the first line of defense for a torn meniscus. These options aim to reduce pain, inflammation, and improve knee function without resorting to surgery.
- RICE: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE) is a common initial treatment for many knee injuries, including a torn meniscus. Resting the injured knee reduces stress and allows for healing. Applying ice to the area helps reduce inflammation and pain. Compression with a bandage can help reduce swelling. Elevating the leg above the heart also helps minimize swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a crucial role in restoring knee function after a meniscus tear. Physical therapists can teach exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve range of motion, and enhance stability. They can also provide guidance on proper biomechanics to prevent further injury.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger pain medications or steroid injections to manage pain and inflammation.
Surgical Procedures, Torn meniscus recovery time
Surgical procedures are considered when conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms or when the tear is significant and impacting knee function. There are two main types of surgical procedures for a torn meniscus: meniscus repair and meniscectomy.
Meniscus Repair
Meniscus repair aims to stitch the torn portion of the meniscus back together. This procedure is typically considered for younger individuals with a tear that is located in a stable part of the meniscus.
- Pros: Preserves the meniscus, which helps maintain knee stability and cushioning. Can be more effective in the long term for younger individuals.
- Cons: Requires a longer recovery period than meniscectomy. Not suitable for all types of tears, especially those involving the outer edge of the meniscus.
Meniscectomy
Meniscectomy involves removing the torn portion of the meniscus. This procedure is often performed when the tear is located in a less stable part of the meniscus or when the tear is too extensive to repair.
- Pros: Quicker recovery time than meniscus repair. Can effectively alleviate pain and improve knee function.
- Cons: Removes a part of the meniscus, which can lead to increased risk of osteoarthritis in the future. May not be as effective in the long term as meniscus repair, especially for younger individuals.
Recovery Process After Surgery
The recovery process after surgery for a torn meniscus depends on the type of procedure performed and the individual’s overall health. It typically involves a period of immobilization followed by a gradual rehabilitation program.
Immobilization
After surgery, the knee may be immobilized with a brace or splint for a few weeks to allow the healing process to begin. This period of immobilization helps to protect the repaired or removed meniscus and prevent further injury.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after meniscus surgery is crucial for regaining full knee function. It involves a gradual progression of exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve range of motion, and enhance stability. The rehabilitation program may include:
- Range of motion exercises: These exercises help to restore the full range of motion in the knee joint. Examples include gentle bending and straightening of the knee, as well as controlled movements in different directions.
- Strengthening exercises: These exercises focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles. Examples include squats, leg presses, and hamstring curls.
- Proprioceptive exercises: These exercises aim to improve balance and coordination, which are essential for stability and preventing further injury. Examples include standing on one leg, walking on uneven surfaces, and performing balance drills.
Pain Management
Pain management is an important part of the recovery process. After surgery, pain medication may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation. As the healing progresses, pain should gradually subside. Physical therapy can also help to reduce pain and improve function.
